Token#
- class miniworldmaker.tokens.token.Token(position=(0, 0), board=None)[source]#
Tokens are objects on your board. Tokens can move around the board and have sensors to detect other tokens.
The appearance of a token is determined by its costume.
Examples
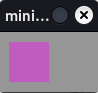
Create a token:
from miniworldmaker import * board = Board() board.size = (100,60) Token(position=(10, 10)) board.run()
Output:
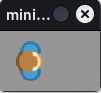
Create a token with an image:
from miniworldmaker import * board = Board(100,60) token = Token((10, 10)) token.add_costume("images/player.png") board.run()
Output:
import miniworldmaker class MyToken(miniworldmaker.Token): def on_setup(self): self.add_costume("images/player.png") board = Board(100,60) my_token = MyToken(position = (40,130)) board.run()
Output:

Create a Token at current mouse position:
from miniworldmaker import * board = Board() @board.register def act(self): Token(self.get_mouse_position()) board.run()

See also
See: Token
See: Shapes
See: TextTokens and NumberTokens
Public Data Attributes:
collision_type specifies how collisions should be checked:
defines layer the token is drawn, if multiple tokens overlap.
Token position in last frame
Returns number of costumes of token, 0 if token has no costume
If a token is flipped, it is mirrored via the y-axis.
Gets the costume of token
Gets the costume manager
Directions are handled exactly as in the Scratch programming language, see: Scratch Wiki
Gets the direction as value in unit circle (0° right, 90° top, 180° left...)
Size of the token
The width of the token in pixels.
The height of the token in pixels.
The x-value of a token
The y-value of a token
x-value of token center-position
x-value of token topleft-position
x-value of token topleft-position
y-value of token center-position
x-value of token center-position
Defines if the costume of a token should be rotatable.
Should token react to events? You can turn this option off for additional performance boost.
The fill color of token as rgba value, e.g.
The fill color of token as rgba value, e.g.
Is token filled with color?
border color of token.
border color of token.
The border-size of token.
The surrounding Rectangle as pygame.Rect.
The image of the token:
The position of the token as Position(x, y)
token_idchildrenspeedaskis_display_initializedInherited from
BaseTokenboarddirtyIf token is dirty, it will be repainted.
rectImplemented in subclass
imageImplemented in subclass
Inherited from
DirtySpritevisibleYou can make this sprite disappear without removing it from the group assign 0 for invisible and 1 for visible
layerLayer property can only be set before the sprite is added to a group, after that it is read only and a sprite's layer in a group should be set via the group's change_layer() method.
Inherited from
SpritelayerDynamic, read only property for protected _layer attribute.
Public Methods:
__init__([position, board])create_on_board(board)Creates a token to a specific board
from_center(center_position)Creates a token with center at center_position
flip_x()Flips the actor by 180° degrees.
add_costume([source])Adds a new costume to token.
add_costumes(sources)Adds multiple costumes
remove_costume([source])Removes a costume from token
switch_costume(source)Switches the costume of token
set_costume(costume)set_background_color(color)Switches to the next costume of token
turn_left([degrees])Turns actor by degrees degrees left
turn_right([degrees])Turns token by degrees degrees right
point_in_direction(direction)Token points in given direction.
point_towards_position(destination)Token points towards a given position
point_towards_token(other)Token points towards another token.
set_size(value)scale_width(value)scale_height(value)move([distance])Moves actor distance steps in current direction
move_vector(vector)Moves actor in direction defined by the vector
move_up([distance])move_down([distance])move_left([distance])move_right([distance])deprecated - use: undo_move()
Undo the last move.
move_towards(target)move_in_direction(direction[, distance])Moves token distance steps into a direction or towards a position
move_to(position)Moves token distance to a specific board_posiition
remove([kill])Removes this token from board
bounce_from_border(borders)The actor "bounces" from a border.
on_not_detecting_board is called, when token is not on the board.
detect_all([token_filter, direction, distance])Detects if tokens are on token position.
detect_tokens([token_filter, direction, ...])Alias of
Token.detect_all()sensing_tokens([token_filter, direction, ...])Alias of
Token.sensing_tokens()detect([token_filter, direction, distance])Senses if tokens are on token position.
detect_token([token_filter, direction, distance])Senses if tokens are on token position.
sensing_token([token_filter, direction, ...])Alias of
Token.detect()detect_borders([distance])Senses borders
sensing_borders([distance])Alias of
Token.sensing_borders()Does the token touch the left border?
Does the token touch the left border?
Alias of
Token.sensing_left_border()Does the token touch the right border?
Does the token touch the right border?
Alias of
Token.sensing_right_border()Does the token touch the lower border?
Does the token touch the lower border?
Alias of
Token.sensing_top_border()Does the token touch the lower border?
Alias of
Token.sensing_bottom_border()Alias of
Token.sensing_bottom_border()detect_color([color])Senses colors in board-background at token center-position
sensing_color([color])Senses colors in board-background at token center-position
detect_colosr([color])Senses colors in board-background at token center-position
detect_color_at([direction, distance])Detects colors in board-background at token-position
sensing_color_at([direction, distance])Detects colors in board-background at token-position
sense_color_at([direction, distance])Detects colors in board-background at token-position
detect_tokens_at([direction, distance, ...])Detects a token in given direction and distance.
sensing_tokens_at([token_filter, direction, ...])Alias of
Token.sensing_tokens_at()detect_token_at([direction, distance, ...])- rtype:
detect_tokens_in_front([token_filter, distance])- rtype:
detect_token_in_front([token_filter, distance])- rtype:
detect_point(position)Is the token colliding with a specific (global) point?
sensing_point(position)Is the token colliding with a specific (global) point?
detect_rect(rect)Is the token colliding with a static rect?
is_touching_rect(rect)Is the token colliding with a static rect?
bounce_from_token(other)animate([speed])animate_costume(costume[, speed])animate_loop([speed])Animates a costume with a looping animation
Stops current animation.
send_message(message)Sends a message to board.
on_key_down(key)on_key_down is called one time when a key is pressed down.
on_key_pressed(key)on_key_pressed is called when while key is pressed.
on_key_up(key)on_mouse_over(position)on_mouse_over is called, when mouse is moved over token :type position: :param position: The mouse position
on_mouse_leave(position)on_mouse_over is called, when mouse is moved over token :type position: :param position: The mouse position
on_mouse_left(position)on_mouse_left is called when left mouse button was pressed.
on_mouse_right(position)Method is called when right mouse button was pressed.
on_mouse_motion(position)Method is called when mouse moves.
on_mouse_left_released(position)Method is called when left mouse key is released.
on_mouse_right_released(position)Method is called when right mouse key is released.
on_message(message)Messages are used to allow objects to communicate with each other.
on_clicked_left(position)The mouse is on top of a token and mouse was clicked.
on_clicked_right(position)The mouse is on top of a token and mouse was clicked.
on_detecting_board is called, when token is on the board
fill(value)Set fill color for borders and lines
hide()Hides a token (the token will be invisible)
show()Displays a token ( an invisible token will be visible)
register(method[, force, name])This method is used for the @register decorator.
- rtype:
Rect
- rtype:
Rect
get_rect()Gets the rect of the token.
__str__()Return str(self).
set_position(value)get_distance_to(obj)Gets the distance to another token or a position
Inherited from
BaseToken__init__([board])set_board(new_board)new_costume()get_costume_class()on_detecting_token(token)on_sensing_token is called, when token is sensing a token on same position
is_detecting_board([distance])Is the token on board if it is moving distance steps forward?
sensing_on_board([distance])Is the token on board if it is moving distance steps forward?
is_sensing_on_board([distance])Is the token on board if it is moving distance steps forward?
on_detecting_borders(borders)on_sensing_border is called, when token is near a border
on_sensing_borders(borders)on_sensing_border is called, when token is near a border
Inherited from
DirtySprite__init__(*groups)__repr__()Return repr(self).
Inherited from
Sprite__init__(*groups)add(*groups)add the sprite to groups
remove(*groups)remove the sprite from groups
add_internal(group)For adding this sprite to a group internally.
remove_internal(group)For removing this sprite from a group internally.
update(*args, **kwargs)method to control sprite behavior
kill()remove the Sprite from all Groups
groups()list of Groups that contain this Sprite
alive()does the sprite belong to any groups
__repr__()Return repr(self).
Private Data Attributes:
_board_sensor_position_manager_costume_manager_collision_type_layer_is_acting_boardPrivate Methods:
_remove_position_manager()_remove_board_sensor()Inherited from
DirtySprite_set_visible(val)set the visible value (0 or 1) and makes the sprite dirty
_get_visible()return the visible value of that sprite
- add_costume(source=None)[source]#
Adds a new costume to token. The costume can be switched with self.switch_costume(index)
- Return type:
- Parameters:
source – Path to the first image of new costume or Tuple with color-value
Examples
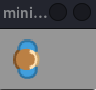
Add first costume from image:
from miniworldmaker import * board = Board((100,60)) token = Token((10,10)) costume = token.add_costume("images/player.png") board.run()
Output:
Add first costume from color:
from miniworldmaker import * board = Board((100,60)) token = Token((10,10)) costume = token.add_costume((255,255,0)) board.run()
Output:

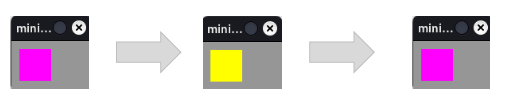
Create two costumes and switch between costumes
from miniworldmaker import * board = Board((100,60)) token = Token((10,10)) board.speed = 30 costume1 = token.add_costume((255,255,0)) costume2 = token.add_costume((255,0,255)) @token.register def act(self): if self.costume == costume1: self.switch_costume(costume2) else: self.switch_costume(costume1) board.run()
Output:
- Returns:
The new costume.
- animate_loop(speed=10)[source]#
Animates a costume with a looping animation
Switches through all costume-images every
speed-frame.Examples
from miniworldmaker import * board = Board(columns=280, rows=100) robo = Token(position=(0, 0)) robo.costume.add_images(["images/1.png", "images/2.png","images/3.png","images/4.png"]) robo.size = (99, 99) robo.animate_loop() board.run()
- Parameters:
speed (int, optional) – Every
speedframe, the image is switched. Defaults to 10.
- property board_sensor#
- property border#
The border-size of token.
The value is 0, if token has no border.
Note
You can also set border with
costume.borderor you can set the border withboard.default_borderExamples
Set border of token:
from miniworldmaker import * board = Board(210,80) board.default_border_color = (0,0, 255) board.default_border = 1 t = Token((10,10)) # default-border and color from bord t.add_costume("images/player.png") t2 = Token ((60, 10)) # overwrites default border values t2.add_costume("images/player.png") t2.border_color = (0,255, 0) t2.border = 5 t3 = Token ((110, 10)) # removes border t3.add_costume("images/player.png") t3.border = None board.run()
Output:

- property border_color#
border color of token.
The border-color is a rgba value, for example (255, 0, 0) for red, (0, 255, 0) for green and (255, 0, 0, 100).
- If the color-value has 4 values, the last value defines the transparency:
0: Full transparent,
255: No transparency
Examples
See
Token.border
- bounce_from_border(borders)[source]#
The actor “bounces” from a border.
The direction is set according to the principle input angle = output angle. :rtype:
TokenNote
You must check for borders first!
- Parameters:
borders – A list of borders as strings e.g. [“left”, “right”]
Examples
from miniworldmaker import * import random board = Board(150, 150) token = Token((50,50)) token.add_costume("images/ball.png") token.direction = 10 @token.register def act(self): self.move() borders = self.sensing_borders() if borders: self.bounce_from_border(borders) board.run()
Output:
- Returns:
The token
- property center_x#
x-value of token center-position
- property center_y#
y-value of token center-position
- class_image: str = ''#
- property collision_type: str#
collision_type specifies how collisions should be checked:
default: tile for TiledBoards, ‘mask’ for PixelBoards
tile: Are tokens on the same tile? (only TiledBoard)
rect: Are tokens colliding when checking their bounding - boxes? (Only PixelBoard)
static-rect: Are tokens colliding when checking circle with radius = bounding-box-radius.(Only PixelBoard)
circle: Are tokens colliding when checking circle with radius = bounding-box-radius.(Only PixelBoard)
mask: Are tokens colliding when checking if their image masks are overlapping.
- property color#
The fill color of token as rgba value, e.g. (255, 0, 0) for red.
When
fill_coloris set to a color, the attributeis_filledof costume (See: :py:attr:.appearances.appearance.Appearance.is_filled`) is set toTrue.Note
Aliases:
Token.colorWarning
If you fill a costume with an image, the image will be completely overwritten, even if fill_color is transparent.
This behaviour may change in later releases!
Examples:
from miniworldmaker import * board = Board(200,80) board.default_fill_color = (0,0, 255) t = Token() t2 = Token((40,0)) t2.is_filled = (0, 255, 0) t3 = Token((80, 0)) t3.fill_colorimport miniworldmaker.tokens.token as token
= (255, 0, 0)
t4 = Token((120, 0)) t4.add_costume((0,0,0)) t4.fill_color = (255, 255, 0)
t5 = Token((160, 0)) t5.add_costume(“images/player.png”) t5.fill_color = (255, 255, 0, 100) # image is overwritten
t6 = Circle((0, 40), 20) t6.position = t6.center t6.fill_color = (255, 255, 255)
t7 = Ellipse((40, 40), 40, 40) t7.fill_color = (255, 0, 255)
board.run()
Output:

- property costume_count: int#
Returns number of costumes of token, 0 if token has no costume
Examples
Add costume and count costumes
from miniworldmaker import * board = Board() token = Token() assert token.costume_count == 0 token.add_costume((255,0,0,0)) assert token.costume_count == 1 board.run()
- Returns:
_description_
- Return type:
- property costume_manager#
- property costumes: CostumesManager#
Gets the costume manager
The costume manager can be iterated to get all costumes
- classmethod create_on_board(board)[source]#
Creates a token to a specific board
overwritten in subclasses
- detect(token_filter=None, direction=0, distance=0)[source]#
Senses if tokens are on token position. Returns the first found token.
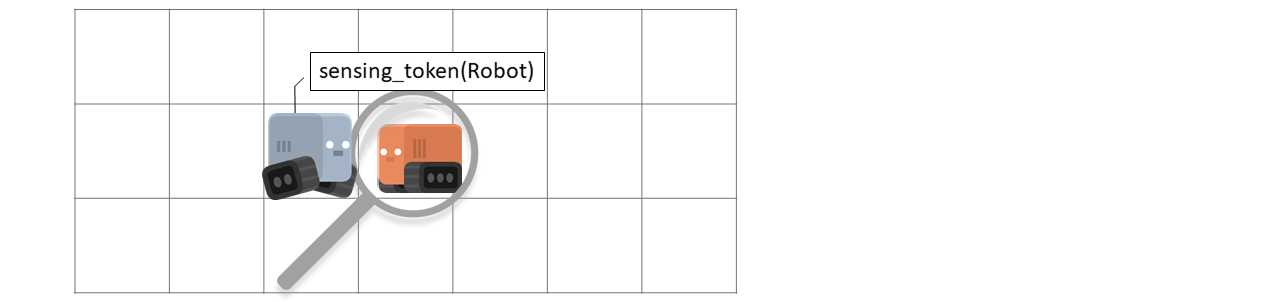
- Parameters:
token_filter – filter by token type. Enter a class_name of tokens to look for heredirection: int = 0, distance: int = 0
direction – The direction in which tokens should be detected.
distance – The distance in which tokens should be detected (Start-Point is token.center)
- Returns:
First token found by Sensor
Examples
The green robot pushes the yellow robot:
from miniworldmaker import * board = TiledBoard(8,3) token = Token((1,1)) token.add_costume("images/robo_green.png") token.orientation = -90 token.direction = 90 token2 = Token((4,1)) token2.add_costume("images/robo_yellow.png") token2.orientation = -90 token2.direction = -90 @token.register def act(self): self.move() token = self.sensing_token() if token: token.move_right() board.run()
Output:
- detect_all(token_filter=None, direction=0, distance=0)[source]#
Detects if tokens are on token position. Returns a list of tokens.
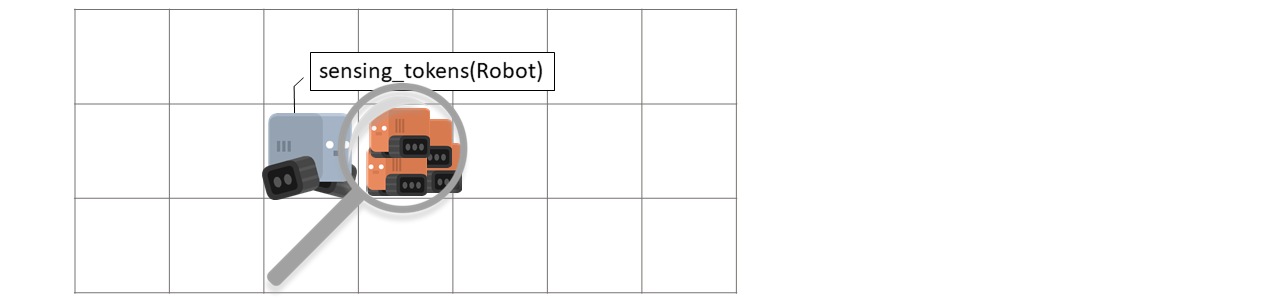
- Parameters:
token_filter – filter by token type. Enter a class_name of tokens to look for here
direction – The direction in which tokens should be detected.
distance – The distance in which tokens should be detected (Start-Point is token.center)
- Returns:
All tokens found by Sensor
- detect_borders(distance=0)[source]#
Senses borders
- Return type:
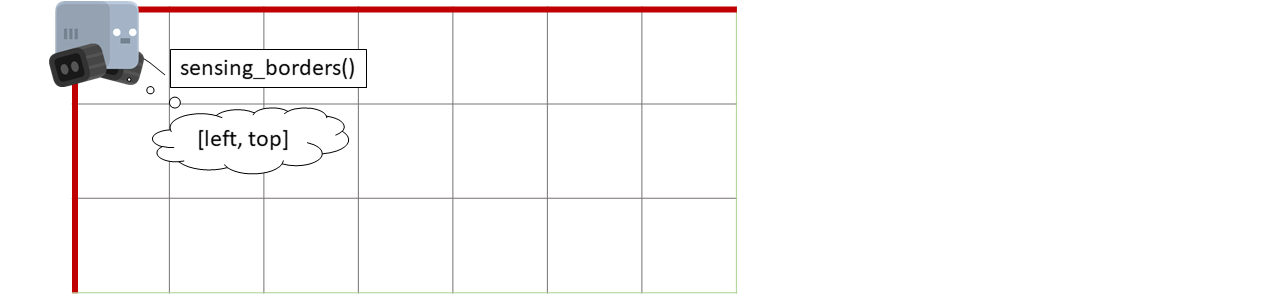
- Parameters:
distance – Specifies the distance in front of the actuator to which the sensors reacts.
- Returns:
True if border was found.
- detect_color(color=None)[source]#
Senses colors in board-background at token center-position
- Return type:
- Parameters:
color – color as tuple
- Returns:
True, if color was found
- detect_color_at(direction=None, distance=0)[source]#
Detects colors in board-background at token-position
- detect_colosr(color=None)[source]#
Senses colors in board-background at token center-position
- Return type:
- Parameters:
color – A list of colors
- Returns:
True, if any color was found
- detect_left_border()[source]#
Does the token touch the left border?
- Return type:
- Returns:
True if border was found.
- detect_point(position)[source]#
Is the token colliding with a specific (global) point?
- Return type:
- Returns:
True if point is below token
- detect_right_border()[source]#
Does the token touch the right border?
- Return type:
- Returns:
True if border was found.
- detect_token(token_filter=None, direction=0, distance=0)#
Senses if tokens are on token position. Returns the first found token.

- Parameters:
token_filter – filter by token type. Enter a class_name of tokens to look for heredirection: int = 0, distance: int = 0
direction – The direction in which tokens should be detected.
distance – The distance in which tokens should be detected (Start-Point is token.center)
- Returns:
First token found by Sensor
Examples
The green robot pushes the yellow robot:
from miniworldmaker import * board = TiledBoard(8,3) token = Token((1,1)) token.add_costume("images/robo_green.png") token.orientation = -90 token.direction = 90 token2 = Token((4,1)) token2.add_costume("images/robo_yellow.png") token2.orientation = -90 token2.direction = -90 @token.register def act(self): self.move() token = self.sensing_token() if token: token.move_right() board.run()
Output:
- detect_tokens(token_filter=None, direction=0, distance=0)#
Alias of
Token.detect_all()
- detect_tokens_at(direction=None, distance=0, token_filter=None)[source]#
Detects a token in given direction and distance.
Examples
from miniworldmaker import * board = Board() wall=Rectangle((200,0)) wall.size = (20, 400) for i in range(7): token = Circle((10,i*60 + 20)) token.range = i * 10 @token.register def act(self): if not self.detect_tokens_at(self.direction, self.range): self.direction = "right" self.move() board.run()
- Parameters:
direction – The direction in which tokens should be detected.
distance – The distance in which tokens should be detected (Start-Point is token.center)
- Return type:
- Returns:
A list of tokens
- detect_top_border()[source]#
Does the token touch the lower border?
- Return type:
- Returns:
True if border was found.
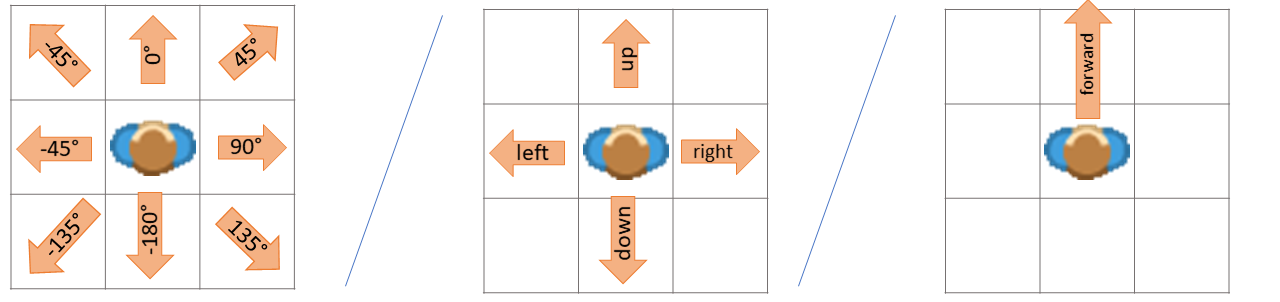
- property direction: int#
Directions are handled exactly as in the Scratch programming language, see: Scratch Wiki
The default direction is
0°. All tokens are looking"up"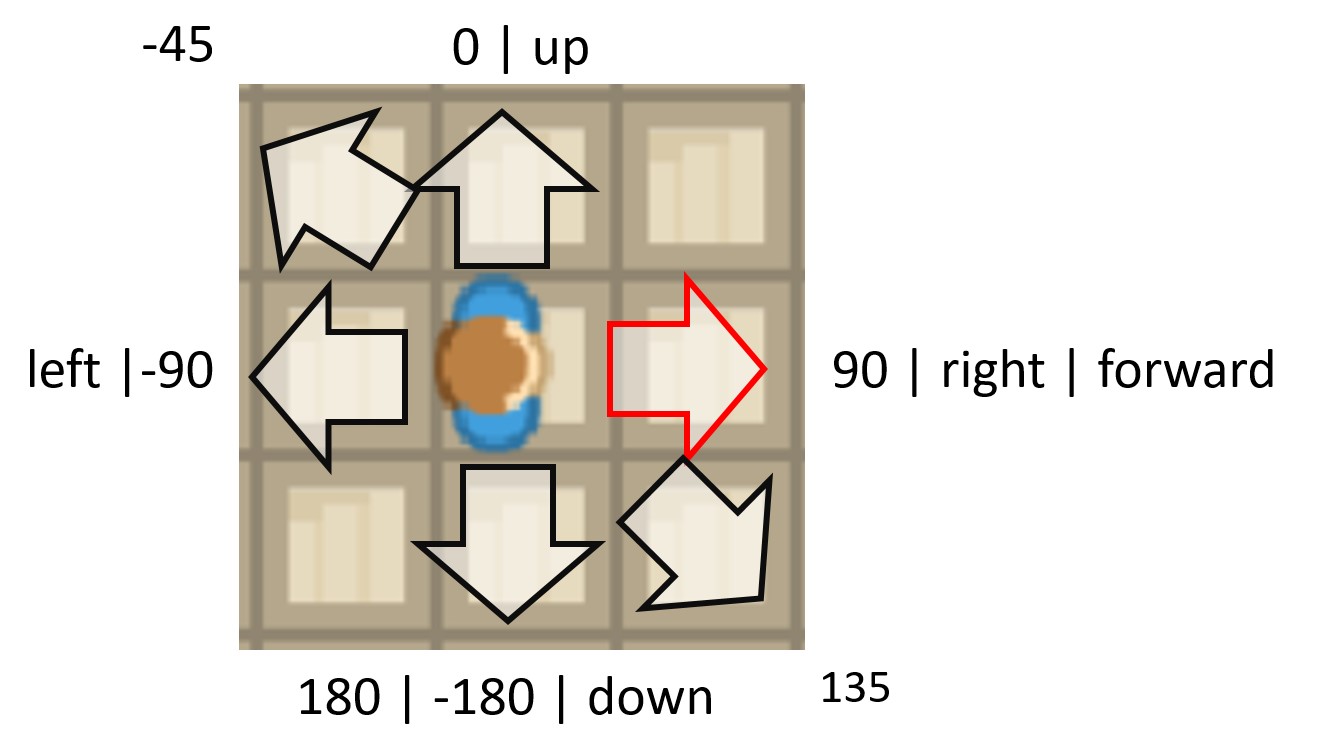
Values for Direction
0°or"up": up90°or"right": Move right-90°or"left": Move left180°or"down": Move down"forward": Current direction
Sets direction of the token.
You can use an integer or a string to describe the direction
- Options
0,"up"- Look up90,"right", - Look right-90,"left", - Look left-180,180,"down"- Look down
Examples
Move in a direction with WASD-Keys
def on_key_down(self, keys): if "W" in keys: self.direction = "up" elif "S" in keys: self.direction = "down" elif "A" in keys: self.direction = "left" elif "D" in keys: self.direction = "right" self.move()
Move 45°:
from miniworldmaker import * board = Board(100, 100) c = Circle ((50,50), 10) @c.register def act(self): c.direction = 45 c.move() board.run()
Move -45°:
from miniworldmaker import * board = Board(100, 100) c = Circle ((50,50), 10) @c.register def act(self): c.direction = -45 c.move() board.run()
- property direction_at_unit_circle: int#
Gets the direction as value in unit circle (0° right, 90° top, 180° left…)
- property fill_color#
The fill color of token as rgba value, e.g. (255, 0, 0) for red.
When
fill_coloris set to a color, the attributeis_filledof costume (See: :py:attr:.appearances.appearance.Appearance.is_filled`) is set toTrue.Note
Aliases:
Token.colorWarning
If you fill a costume with an image, the image will be completely overwritten, even if fill_color is transparent.
This behaviour may change in later releases!
Examples:
from miniworldmaker import * board = Board(200,80) board.default_fill_color = (0,0, 255) t = Token() t2 = Token((40,0)) t2.is_filled = (0, 255, 0) t3 = Token((80, 0)) t3.fill_colorimport miniworldmaker.tokens.token as token
= (255, 0, 0)
t4 = Token((120, 0)) t4.add_costume((0,0,0)) t4.fill_color = (255, 255, 0)
t5 = Token((160, 0)) t5.add_costume(“images/player.png”) t5.fill_color = (255, 255, 0, 100) # image is overwritten
t6 = Circle((0, 40), 20) t6.position = t6.center t6.fill_color = (255, 255, 255)
t7 = Ellipse((40, 40), 40, 40) t7.fill_color = (255, 0, 255)
board.run()
Output:

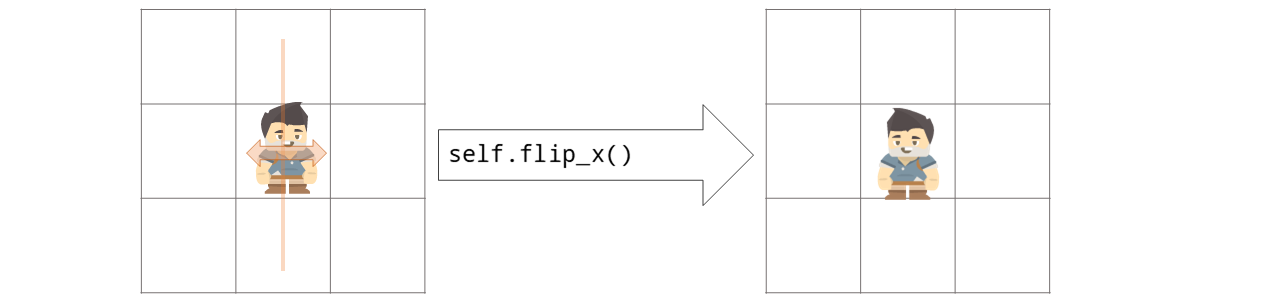
- flip_x()[source]#
Flips the actor by 180° degrees. The costume is flipped and the token’s direction changed by 180 degrees.
- Return type:
Examples
Flip a token in Example flipthefish.py
from miniworldmaker import * board=TiledBoard() board.columns = 4 board.rows = 1 board.add_background("images/water.png") fish = Token() fish.border = 1 fish.add_costume("images/fish.png") fish.direction = "right" fish.orientation = -90 @fish.register def act(self): self.move() @fish.register def on_not_detecting_board(self): self.move_back() self.flip_x() board.run()
Output:
- classmethod from_center(center_position)[source]#
Creates a token with center at center_position
- Parameters:
center_position – Center of token
- get_rect()[source]#
Gets the rect of the token.
If a camera is used, the local rect is written.
- Return type:
Rect- Returns:
A Rectangle with local position.
- Return type:
pygame.Rect
- property height#
The height of the token in pixels.
When the height of a token is changed, the width is scaled proportionally.
Examples
Create a token and scale width/height proportionally:
from miniworldmaker import * board = Board(800,400) def create_token(x, y): t = Token() t.position = (x, y) t.add_costume("images/alien1.png") t.border = 1 return t t0 = create_token(0,0) t1 = create_token(50,0) t1.height = 400 t2 = create_token(300,0) t2.width = 180 board.run()

- property image: Surface#
The image of the token:
Warning
Warning: You should not directly draw on the image as the image will be reloaded during animations
- property is_filled#
Is token filled with color?
- property is_flipped: bool#
If a token is flipped, it is mirrored via the y-axis. You can use this property in 2d-plattformers to change the direction of token.
Note
It may be necessary to set
is_rotatable = TrueExamples
Flip a costume after 100 frames.
from miniworldmaker import * board = Board(100,100) token = Token() token.add_costume("images/alien1.png") token.height= 400 token.width = 100 token.is_rotatable = False @token.register def act(self): if self.board.frame % 100 == 0: if self.is_flipped: self.is_flipped = False else: self.is_flipped = True board.run()
Output:
- Returns:
True, if token is flipped
- property is_rotatable: bool#
Defines if the costume of a token should be rotatable. The token can still be rotated with the
directionproperty, but its costume won’t be changedNote
You can also use
token.costume.is_rotatableExamples
Create a rotatable and a not rotatable token
from miniworldmaker import * board = Board() t1 = Token((100,100)) t1.add_costume("images/alien1.png") t2 = Token((200,200)) t2.add_costume("images/alien1.png") t2.is_rotatable = False @t1.register def act(self): self.move() self.direction += 1 @t2.register def act(self): self.move() self.direction += 1 board.run()
Output:
- is_sensing_bottom_border()#
Alias of
Token.sensing_bottom_border()- Return type:
- is_sensing_left_border()#
Alias of
Token.sensing_left_border()- Return type:
- is_sensing_right_border()#
Alias of
Token.sensing_right_border()- Return type:
- is_sensing_top_border()#
Alias of
Token.sensing_top_border()- Return type:
- is_touching_bottom_border()#
Alias of
Token.sensing_bottom_border()- Return type:
- is_touching_rect(rect)#
Is the token colliding with a static rect?
- property local_center#
x-value of token center-position
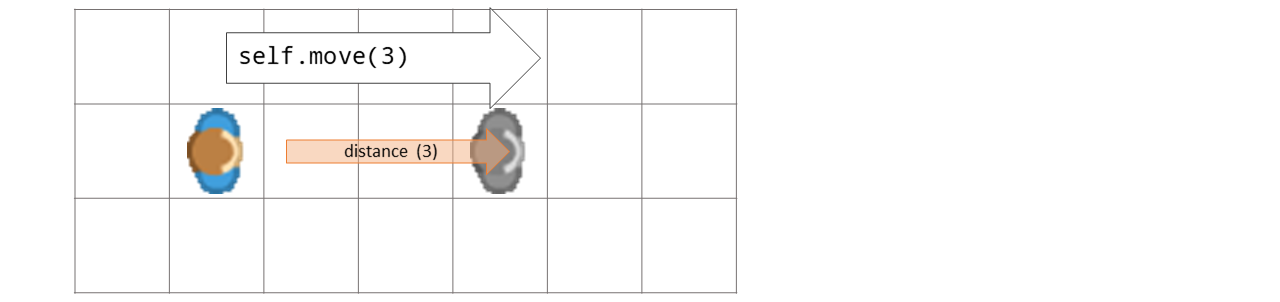
- move(distance=0)[source]#
Moves actor distance steps in current direction
- Parameters:
distance – Number of steps to move. If distance = 0, the actor speed will be used.
- Returns:
The moved token
Examples
if token is on the board, move forward:
class Robot(Token): def act(self): if self.detecting_board(): self.move()
- move_back()[source]#
deprecated - use: undo_move()
In next versions, this functions will move the token backwards
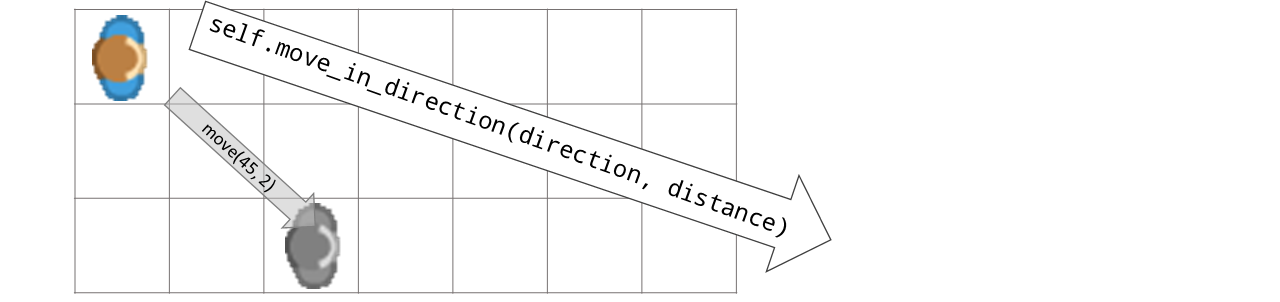
- move_in_direction(direction, distance=1)[source]#
Moves token distance steps into a direction or towards a position
- Options
0, “up” - Look up
90, “right”, - Look right
-90, “left”, - Look left
-180, 180, “down” - Look down

- Parameters:
direction – Direction as angle
distance – Senses obj “distance” steps in front of current token.
- Returns:
The token itself
- move_to(position)[source]#
Moves token distance to a specific board_posiition
- Parameters:
position – The position to which the actor should move. The position can be a 2-tuple (x, y)
board_position (which will be converted to a) –
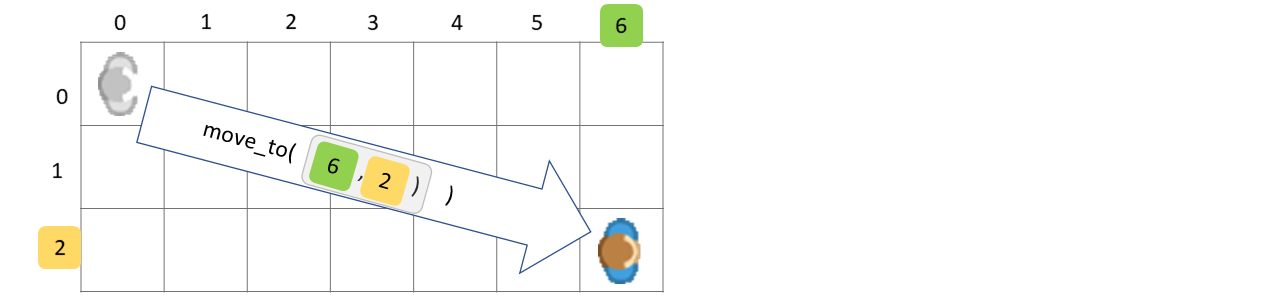
- Returns:
The token itself
Examples
move to (3, 2) on mouse_click
def on_clicked_left(self, position): self.move_to((3,2))
- move_vector(vector)[source]#
Moves actor in direction defined by the vector
- Returns:
The moved token
- on_clicked_left(position)[source]#
The mouse is on top of a token and mouse was clicked.
Examples
Registering a on_click event:
token = miniworldmaker.Token((2,2)) @token.register def on_clicked_left(self, position): print("clicked" + str(position))
- Parameters:
position (tuple) – Actual mouse position as tuple (x,y)
- Raises:
NotImplementedOrRegisteredError – The error is raised when method is not overwritten or registered.
- on_clicked_right(position)[source]#
The mouse is on top of a token and mouse was clicked.
Examples
Registering a on_click event:
token = miniworldmaker.Token((2,2)) @token.register def on_clicked_right(self, position): print("clicked" + str(position))
- Parameters:
position (tuple) – Actual mouse position as tuple (x,y)
- Raises:
NotImplementedOrRegisteredError – The error is raised when method is not overwritten or registered.
- on_detecting_board()[source]#
on_detecting_board is called, when token is on the board
Examples
Register on_detecting_board method:
@player.register def on_detecting_board(self): print("Player 3: I'm on the board:")
- Raises:
NotImplementedOrRegisteredError – The error is raised when method is not overwritten or registered.
- on_key_down(key)[source]#
on_key_down is called one time when a key is pressed down.
Note
Instead of on_key_down you can use on_key_down_letter, e.g. on_key_down_a or on_key_down_w , if you want to handle an on_key_down event for a specific letter.
Examples
Register a key_down event:
token1 = miniworldmaker.Token(position = (2, 2) ) token1.add_costume((100,0,100,100)) @token1.register def on_key_down(self, key): print(key)
Register on_key_down_a event
token1 = miniworldmaker.Token(position = (2, 2) ) token1.add_costume((100,0,100,100)) @token1.register def on_key_down_a(self): print("a")
- Parameters:
key (list) – The typed key as list (e.g. [‘A’, ‘a’]) containing both uppercase and lowercase of typed letter.
- Raises:
NotImplementedOrRegisteredError – The error is raised when method is not overwritten or registered.
- on_key_pressed(key)[source]#
on_key_pressed is called when while key is pressed. If you hold the key, on_key_pressed is repeatedly called again and again until the key is released.
Note
Like on_key_down the method can be called in the variant on_key_pressed_[letter] (e.g. on_key_pressed_w(self)).
Examples
Register on_key_pressed event:
token1 = miniworldmaker.Token(position = (2, 2) ) token1.add_costume((100,0,100,100)) @token1.register def on_key_pressed(self, key): print("pressed", key) @token1.register def on_key_pressed_s(self): print("pressed s")
- Parameters:
key (list) – The typed key as list (e.g. [‘C’, ‘c’, ‘D’, ‘d’]) containing both uppercase and lowercase
letter. (of typed) –
- Raises:
NotImplementedOrRegisteredError – The error is raised when method is not overwritten or registered.
- on_message(message)[source]#
Messages are used to allow objects to communicate with each other.
Send a message:
A token and the board can send a message to all tokens and the board with the command: self.send_message(“message_string”)
Process a message:
If your board or your token should react to messages you can use the event on_message:
Examples
Receive a message:
@player.register def on_message(self, message): if message == "Example message": do_something()
- Parameters:
message (str) – The message as string
- Raises:
NotImplementedOrRegisteredError – The error is raised when method is not overwritten or registered.
- on_mouse_leave(position)[source]#
on_mouse_over is called, when mouse is moved over token :type position: :param position: The mouse position
- on_mouse_left(position)[source]#
on_mouse_left is called when left mouse button was pressed. You must register or implement this method as an event.
Note
The event is triggered, when mouse-left was clicked, even when the current mouse position is not related to token position.
You can use
Token.sensing_point()to check, if the mouse_position is inside the token.Examples
A circle will be moved, if you click on circle.
from miniworldmaker import * board = Board(120,40) circle = Circle((20, 20)) circle.direction = 90 @circle.register def on_mouse_left(self, mouse_pos): if self.sensing_point(mouse_pos): self.move() board.run()
- Parameters:
position (tuple) – Actual mouse position as tuple (x,y)
- Raises:
NotImplementedOrRegisteredError – The error is raised when method is not overwritten or registered.
- on_mouse_left_released(position)[source]#
Method is called when left mouse key is released.
Examples
You can use on_mouse_left_release to implement a drag_and_drop event
from miniworldmaker import * board = Board(200, 200) circle = Circle((30, 30), 60) circle.direction = 90 circle.dragged = False @circle.register def on_mouse_left(self, mouse_pos): if self.sensing_point(mouse_pos): self.dragged = True @circle.register def on_mouse_left_released(self, mouse_pos): if not board.is_mouse_pressed(): self.dragged = False self.center = mouse_pos board.run()
Output:
- Parameters:
position (tuple) – Actual mouse position as tuple (x,y)
- Raises:
NotImplementedOrRegisteredError – The error is raised when method is not overwritten or registered.
- on_mouse_motion(position)[source]#
Method is called when mouse moves. You must register or implement this method as an event.
Note
The event is triggered, when mouse is moved, even when the current mouse position is not related to token position.
You can use
Token.sensing_point()to check, if the mouse_position is inside the token.Examples
A circle will be moved, if you click on circle.
from miniworldmaker import * board = Board(120,40) circle = Circle((20, 20)) circle.direction = 90 @circle.register def on_mouse_motion(self, mouse_pos): if self.sensing_point(mouse_pos): self.move() board.run()
- Parameters:
position (tuple) – Actual mouse position as tuple (x,y)
- Raises:
NotImplementedOrRegisteredError – The error is raised when method is not overwritten or registered.
- on_mouse_over(position)[source]#
on_mouse_over is called, when mouse is moved over token :type position: :param position: The mouse position
- on_mouse_right(position)[source]#
Method is called when right mouse button was pressed. You must register or implement this method as an event.
Note
The event is triggered, when mouse was clicked,even when the current mouse position is not related to token position.
You can use
Token.sensing_point()to check, if the mouse_position is inside the token.Examples
See:
Token.on_mouse_left().- Parameters:
position (tuple) – Actual mouse position as tuple (x,y)
- Raises:
NotImplementedOrRegisteredError – The error is raised when method is not overwritten or registered.
- on_mouse_right_released(position)[source]#
Method is called when right mouse key is released. See
Token.on_mouse_left_released().- Parameters:
position (tuple) – Actual mouse position as tuple (x,y)
- Raises:
NotImplementedOrRegisteredError – The error is raised when method is not overwritten or registered.
- on_not_detecting_board()[source]#
on_not_detecting_board is called, when token is not on the board.
Examples
Register on_not_detecting_board method:
@player.register def on_not_detecting_board(self): print("Warning: I'm not on the board!!!")
- Raises:
NotImplementedOrRegisteredError – The error is raised when method is not overwritten or registered.
- point_in_direction(direction)[source]#
Token points in given direction.
You can use a integer or a string to describe the direction
- Return type:
- Parameters:
string (The direction as integer or) –
- Options
0,"up"- Look up90,"right", - Look right-90,"left", - Look left-180,180,"down"- Look down

Examples
Move in a direction with WASD-Keys
def on_key_down(self, keys): if "W" in keys: self.direction = "up" elif "S" in keys: self.direction = "down" elif "A" in keys: self.direction = "left" elif "D" in keys: self.direction = "right" self.move()
- point_towards_position(destination)[source]#
Token points towards a given position
- Return type:
- Parameters:
destination – The position to which the actor should pointing
- Returns:
The new direction
Examples
Point towards mouse_position:
def act(self): mouse = self.board.get_mouse_position() if mouse: self.point_towards_position(mouse) self.move()
- point_towards_token(other)[source]#
Token points towards another token.
- Return type:
- Parameters:
other – The other token
- Returns:
The new direction
- property position_manager#
- property rect: Rect#
The surrounding Rectangle as pygame.Rect. Warning: If the token is rotated, the rect vertices are not the vertices of the token image.
- register(method, force=False, name=None)[source]#
This method is used for the @register decorator. It adds a method to an object
- Parameters:
method (callable) – The method which should be added to the token
force – Should register forced, even if method is not handling a valid event?
name – Registers method with specific name
- remove(kill=True)[source]#
Removes this token from board
Examples
Removes robots in thecrash.py :
def act(self): self.move() other = self.sensing_token(distance = 0, token_type=Robot) if other: explosion = Explosion(position=self.position) self.remove() other.remove()
- remove_costume(source=None)[source]#
Removes a costume from token
- Parameters:
source – The index of the new costume or costume-object. Defaults to actual costume
- send_message(message)[source]#
Sends a message to board.
The message can be received with the
on_message-eventExamples
Send and receive messages:
from miniworldmaker import * board = Board() token1 = Token((2, 2)) token1.add_costume((100,0,100,100)) @token1.register def on_message(self, message): print("Received message:" + message) token2 = Token((100,100)) token2.send_message("Hello from token2") @token2.register def on_key_down_s(self): self.send_message("Hello") board.run()
- Parameters:
message (str) – A string containing the message.
- sense_color_at(direction=None, distance=0)#
Detects colors in board-background at token-position
- sensing_borders(distance=0)#
Alias of
Token.sensing_borders()- Return type:
- sensing_bottom_border()[source]#
Does the token touch the lower border?
- Return type:
- Returns:
True if border was found.
- sensing_color(color=None)#
Senses colors in board-background at token center-position
- Return type:
- Parameters:
color – color as tuple
- Returns:
True, if color was found
- sensing_color_at(direction=None, distance=0)#
Detects colors in board-background at token-position
- sensing_left_border()#
Does the token touch the left border?
- Return type:
- Returns:
True if border was found.
- sensing_point(position)#
Is the token colliding with a specific (global) point?
- Return type:
- Returns:
True if point is below token
- sensing_right_border()#
Does the token touch the right border?
- Return type:
- Returns:
True if border was found.
- sensing_token(token_filter=None, direction=0, distance=0)#
Alias of
Token.detect()
- sensing_tokens(token_filter=None, direction=0, distance=0)#
Alias of
Token.sensing_tokens()
- sensing_tokens_at(token_filter=None, direction=0, distance=0)#
Alias of
Token.sensing_tokens_at()
- sensing_top_border()#
Does the token touch the lower border?
- Return type:
- Returns:
True if border was found.
- property static#
Should token react to events? You can turn this option off for additional performance boost.
- property sticky#
- stop_animation()[source]#
Stops current animation. Costume
is_animatedis set to FalseExamples
from miniworldmaker import * board = Board(columns=280, rows=100) robo = Token(position=(0, 0)) robo.costume.add_images(["images/1.png", "images/2.png","images/3.png","images/4.png"]) robo.size = (99, 99) robo.animate_loop() @timer(frames = 100) def stop(): robo.stop_animation() board.run()
- property stroke_color#
border color of token.
The border-color is a rgba value, for example (255, 0, 0) for red, (0, 255, 0) for green and (255, 0, 0, 100).
- If the color-value has 4 values, the last value defines the transparency:
0: Full transparent,
255: No transparency
Examples
See
Token.border
- switch_costume(source)[source]#
Switches the costume of token
- Return type:
- Parameters:
source – Number of costume or Costume object
Examples
Switch a costume:
from miniworldmaker import * board = Board(100,60) t = Token() costume =t1.add_costume("images/1.png") t.add_costume("images/2.png") t.switch_costume(1) @timer(frames = 40) def switch(): t1.switch_costume(0) board.run()
- Returns:
The new costume
- token_count: int = 0#
- property topleft_x#
x-value of token topleft-position
- property topleft_y#
x-value of token topleft-position
- turn_left(degrees=90)[source]#
Turns actor by degrees degrees left
- Return type:
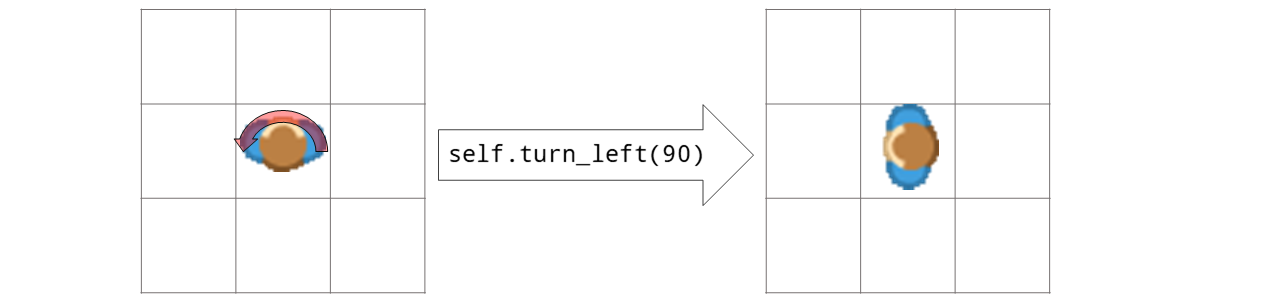
- Options:
You can set the value token.is_rotatable = False if you don’t want the token to be rotated.
Examples
from miniworldmaker import * board = Board(100, 100) t = Token() t.add_costume("images/arrow.png") t.size = (100,100) @t.register def act(self): t.turn_left(1) board.run()
Output:
- Parameters:
degrees – degrees in left direction
- Returns:
New direction
- turn_right(degrees=90)[source]#
Turns token by degrees degrees right
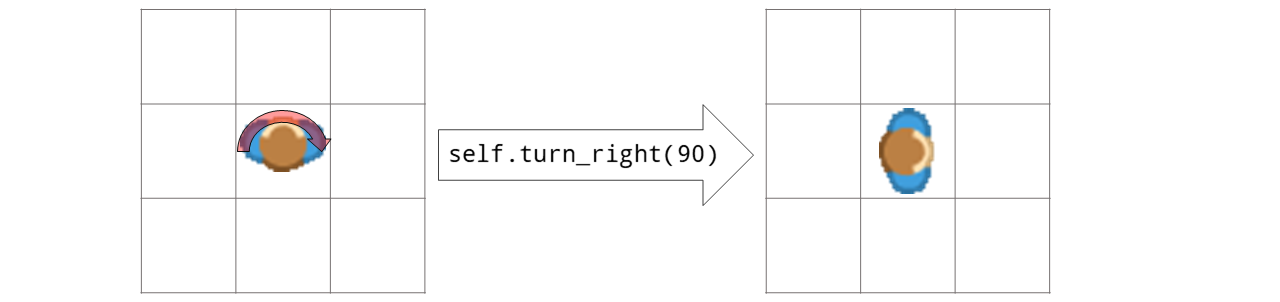
Examples
from miniworldmaker import * board = Board(100, 100) t = Token() t.add_costume("images/arrow.png") t.size = (100,100) @t.register def act(self): t.turn_left(1) board.run()
Output:
- Options:
You can set the value token.is_rotatable = False if you don’t want the token to be rotated.
- Parameters:
degrees – degrees in left direction
- Returns:
New direction
- undo_move()[source]#
Undo the last move. Moves the actor to the last position and resets direction.
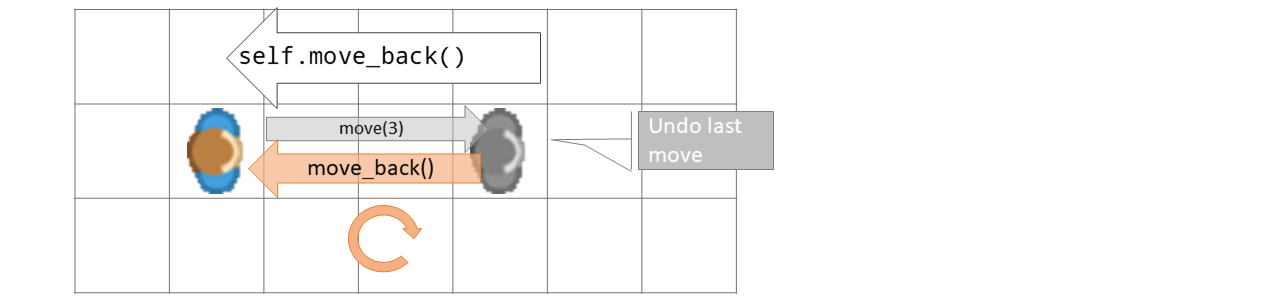
- Returns:
The moved token
Examples
move_back when field is blocked:
def on_sensing_wall(self, wall): self.undo_move()
- property width#
The width of the token in pixels.
When the width of a token is changed, the height is scaled proportionally.
Examples
Create a token and scale width/height proportionally:
from miniworldmaker import * board = Board(800,400) def create_token(x, y): t = Token() t.position = (x, y) t.add_costume("images/alien1.png") t.border = 1 return t t0 = create_token(0,0) t1 = create_token(50,0) t1.height = 400 t2 = create_token(300,0) t2.width = 180 board.run()
