Board#
`Board is the base class for boards.
Warning
If you instanciate a Board, it will be handled as PixelBoard`. You can’t create instances of BaseBoard
Board#
- class miniworldmaker.boards.board_templates.pixel_board.board.Board(view_x=400, view_y=400, tile_size=1)[source]#
A board is a playing field on which tokens can move.
A board has a background and provides basic functions for the positioning of tokens and for the collision detection of tokens, which can be queried via the sensors of the tokens.
You can create your own board by creating a class that inherits from Board or you can directly create a board object of type Board or one of its child classes (TiledBoard, PhysicsBoard, …).
Board
A board for pixel accurate games.
The position of a token on a Board is the pixel at topleft of token.
New tokens are created with top-left corner of token rect at position.
Two tokens collide when their sprites overlap.
Other Boards:
TiledBoard: For Boards using Tiles, like rogue-like rpgs, see TiledBoard)
PhysicsBoard: For Boards using the PhysicsEngine, see PhysicsBoard)
Examples
Creating a TiledBoard Object:
from miniworldmaker import * my_board = TiledBoard() my_board.columns = 30 my_board.rows = 20 my_board.tile_size = 20
Creating a TiledBoard-Subclass.
import miniworldmaker class MyBoard(miniworldmaker.TiledBoard): def on_setup(self): self.columns = 30 self.rows = 20 self.tile_size = 20
Creating a Board Object:
from miniworldmaker import * my_board = Board() my_board.columns = 300 my_board.rows = 200
Creating a Board Subclass
import miniworldmaker class MyBoard(miniworldmaker.Board): def on_setup(self): self.columns = 300 self.rows = 200
See also
See: Board
See: TiledBoard
- Parameters:
view_x – columns of new board (default: 40)
view_y – rows of new board (default:40)
tile_size – Size of tiles (1 for normal Boards, can differ for TiledBoards)
Public Data Attributes:
speed defines how often the method
act()will be called.Frames per second shown on the screen.
Gets width of board in pixels.
Gets height of board in pixels.
The x-boundary (defaults to view_size)
The y-boundary (defaults to view_size)
The y-boundary (defaults to view_size)
Tile size of each tile, if board has tiles
Set the size of board
Set default fill color for borders and lines
Set default stroke color for borders and lines.
Set default border color for borders and lines.
Sets default border color for tokens
A list of all tokens registered to the board.
Returns all backgrounds of the board as list.
Returns the current background
The width of the container
The height of the container
The current displayed image
Inherited from
BaseBoardsubclassessurfaceclass_namewindowGets the parent window
Inherited from
Containersurfacecontainer_widthcontainer_heightwindowsizerecttopleftwindow_docking_positionwidthheightPublic Methods:
__init__([view_x, view_y, tile_size])Checks if position is on the board.
is_position_on_board(pos)Checks if position is on the board.
contains_position(pos)Checks if position is on the board.
contains_rect(rect)Detects if rect is completely on the board.
borders(value)Gets all borders from a source (Position or Rect).
set_tile_size(value)default_fill(value)Set default fill color for borders and lines
Returns the current background
switch_background(background)Switches the background
remove_background([background])Removes a background from board
set_background(source)Adds a new background to the board
add_background(source)Adds a new background to the board
start()Starts the board, if board is not running.
stop([frames])Stops the board.
clear()Alias of
cleanclean()removes all tokens
run([fullscreen, fit_desktop, replit, ...])The method show() should always be called at the end of your program.
play_sound(path)plays sound from path
play_music(path)plays a music from path
stops a music
Gets the current mouse_position
Gets x-coordinate of mouse-position
Gets y-coordinate of mouse-position
gets mouse-position of last frame
Returns True, if mouse is pressed
Returns True, if mouse left button is pressed
Returns True, if mouse right button is pressed
send_message(message[, data])Sends broadcast message
quit([exit_code])quits app and closes the window
reset()Resets the board Creates a new board with init-function - recreates all tokens and actors on the board.
switch_board(new_board)Switches to another board
get_color_from_pixel(position)Returns the color at a specific position
get_from_pixel(position)Gets Position from pixel
Alias for get_from_pixel
to_pixel(position)on_setup()Overwrite or register this method to call on_setup-Actions
__str__()Return str(self).
add_to_board(token, position)Adds a Token to the board.
detect_tokens(position)Gets all tokens which are found at a specific position.
get_tokens_at_position(position)Gets all tokens which are found at a specific position.
get_tokens_from_pixel(pixel)repaint()Implemented in subclasses
update()The mainloop, called once per frame.
handle_event(event[, data])Event handling
register(method)Used as decorator e.g.
unregister(method)direction(point1, point2)distance_to(pos1, pos2)direction_to(pos1, pos2)- rtype:
Inherited from
BaseBoard__init__()get_token_connector(token)- rtype:
TokenConnector
add_container(container, dock[, size])add_board(position, board[, width])remove_container(container)load_board_from_db(file)Loads a sqlite db file.
load_tokens_from_db(file, token_classes)Loads all tokens from db.
save_to_db(file)Saves the current board an all actors to database.
screenshot([filename])Creates a screenshot in given file.
get_background()Implemented in subclass
get_columns_by_width(width)get_rows_by_height(height)Inherited from
Container__init__()on_change()implemented in subclasses
add_to_window(app, dock[, size])update_width_and_height()repaint()Implemented in subclasses
blit_surface_to_window_surface()remove()Implemented in subclasses
handle_event(event, data)get_event(event, data)Implemented in subclasses
is_in_container(x[, y])- rtype:
position_is_in_container(pos)- rtype:
update()Implemented in subclasses
get_local_position(position)- rtype:
Private Methods:
_create_event_manager()_act_all()Overwritten in subclasses, e.g.
_tick_timed_objects()Inherited from
BaseBoard_get_camera_manager_class()_get_token_connector_class()needed by get_token_connector in parent class
- add_background(source)[source]#
Adds a new background to the board
If multiple backgrounds are added, the last adds background will be set as active background.
- Return type:
- Parameters:
source – The path to the first image of the background or a color (e.g. (255,0,0) for red or “images/my_background.png” as path to a background.
Examples
Add multiple Backgrounds:
from miniworldmaker import * board = Board() board.add_background((255, 0 ,0)) # red board.add_background((0, 0 ,255)) # blue board.run() # Shows a blue board.
- Returns:
The new created background.
- property background: Background#
Returns the current background
- borders(value)[source]#
Gets all borders from a source (Position or Rect).
- Return type:
- Parameters:
value – Position or rect
- Returns:
A list of borders, e.g. [“left”, “top”], if rect is touching the left a top border.
- property camera_x#
- property camera_y#
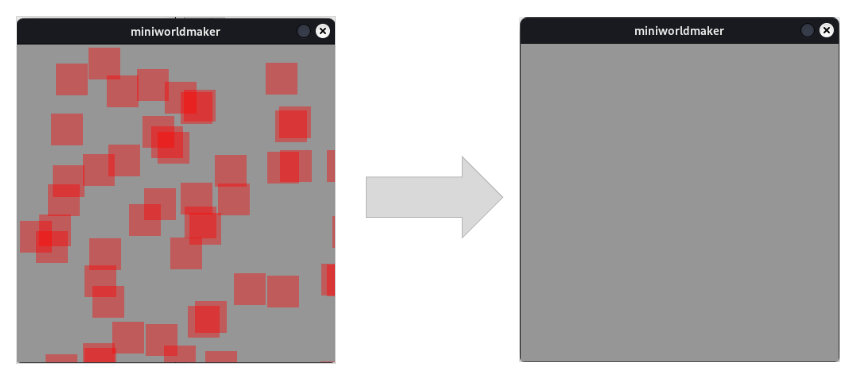
- clean()[source]#
removes all tokens
Examples
Clear a board:
from miniworldmaker import * import random board = Board() for i in range(50): Token((random.randint(0,board.width), random.randint(0,board.height))) @timer(frames = 50) def clean(): board.clear() board.run()
Output:
- clear()[source]#
Alias of
cleansee:
Board.clean()
- property color#
- contains_position(pos)#
Checks if position is on the board.
- Returns:
True, if Position is on the board.
- contains_rect(rect)[source]#
Detects if rect is completely on the board.
- Parameters:
rect – A rectangle as tuple (top, left, width, height)
- property default_border#
Sets default border color for tokens
Note
You must also set a border for token.
Examples
Set default border for tokens:
from miniworldmaker import * board = Board(210,80) board.default_border_color = (0,0, 255) board.default_border = 1 t = Token((10,10)) board.run()
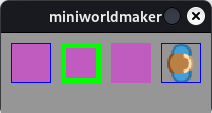
- property default_border_color#
Set default border color for borders and lines.
Note
board.default_border_colordoes not have an effect, if no border is set.You must also set
board.border> 0.Examples
Create tokens with and without with border
from miniworldmaker import * board = Board(210,80) board.default_border_color = (0,0, 255) board.default_border = 1 t = Token((10,10)) t2 = Token ((60, 10)) t2.border_color = (0,255, 0) t2.border = 5 # overwrites default border t3 = Token ((110, 10)) t3.border = None # removes border t4 = Token ((160, 10)) t4.add_costume("images/player.png") # border for sprite board.run()
Output:
- property default_fill_color#
Set default fill color for borders and lines
- property default_is_filled#
- property default_stroke_color#
Set default stroke color for borders and lines. (equivalent to border-color)
- detect_tokens(position)[source]#
Gets all tokens which are found at a specific position.
- Return type:
- Parameters:
position – Position, where tokens should be searched.
- Returns:
A list of tokens
Examples
Get all tokens at mouse position:
position = board.get_mouse_position() tokens = board.get_tokens_by_pixel(position)
- property fill_color#
- property fps: int#
Frames per second shown on the screen.
This controls how often the screen is redrawn. However, the game logic can be called more often or less often independently of this with
board.speed.Examples
board.speed = 10 board.fps = 24 def act(self): nonlocal i i = i + 1 if board.frame == 120: test_instance.assertEqual(i, 13) test_instance.assertEqual(board.frame, 120)
- get_color_from_pixel(position)[source]#
Returns the color at a specific position
Examples: :rtype:
tuple- Parameters:
position – The position to search for
- Returns:
The color
- get_from_pixel(position)[source]#
Gets Position from pixel
PixelBoard: the pixel position is returned TiledBoard: the tile-position is returned
- get_mouse_position()[source]#
Gets the current mouse_position
- Return type:
- Returns:
Returns the mouse position if mouse is on the board. Returns None otherwise
Examples
Create circles at current mouse position:
from miniworldmaker import * board = PixelBoard() @board.register def act(self): c = Circle(board.get_mouse_position(), 40) c.color = (255,255,255, 100) c.border = None board.run()
Output:

- get_tokens_at_position(position)#
Gets all tokens which are found at a specific position.
- Return type:
- Parameters:
position – Position, where tokens should be searched.
- Returns:
A list of tokens
Examples
Get all tokens at mouse position:
position = board.get_mouse_position() tokens = board.get_tokens_by_pixel(position)
- property image: Surface#
The current displayed image
- is_position_on_board(pos)#
Checks if position is on the board.
- Returns:
True, if Position is on the board.
- is_position_on_the_board(pos)[source]#
Checks if position is on the board.
- Returns:
True, if Position is on the board.
- remove_background(background=None)[source]#
Removes a background from board
- Parameters:
background – The index of the new background. Defaults to -1 (last background) or an Appearance
- reset()[source]#
Resets the board Creates a new board with init-function - recreates all tokens and actors on the board.
Examples
Restarts flappy the bird game after collision with pipe:
def on_sensing_collision_with_pipe(self, other, info): self.board.is_running = False self.board.reset()
- run(fullscreen=False, fit_desktop=False, replit=False, event=None, data=None)[source]#
The method show() should always be called at the end of your program. It starts the mainloop.
Examples
A minimal miniworldmaker-program:
from miniworldmaker import * board = TiledBoard() token = Token() board.run()
Output:
- send_message(message, data=None)[source]#
Sends broadcast message
A message can be received by the board or any token on board
- set_background(source)[source]#
Adds a new background to the board
If multiple backgrounds are added, the last adds background will be set as active background.
- Return type:
- Parameters:
source – The path to the first image of the background or a color (e.g. (255,0,0) for red or “images/my_background.png” as path to a background.
Examples
Add multiple Backgrounds:
from miniworldmaker import * board = Board() board.add_background((255, 0 ,0)) # red board.add_background((0, 0 ,255)) # blue board.run() # Shows a blue board.
- Returns:
The new created background.
- property size: tuple#
Set the size of board
Examples
Create a board with 800 columns and 600 rows:
board = miniworldmaker.PixelBoard() board.size = (800, 600)
- property speed: int#
speed defines how often the method
act()will be called.If e.g.
speed = 30, the game logic will be called every 30th-frame.Note
You can adjust the frame-rate with
board.fpsExamples
Set speed and fps.
from miniworldmaker import * board = Board() board.size = (120,210) @board.register def on_setup(self): board.fps = 1 board.speed = 3 @board.register def act(self): board.run()
Output:
` 3 6 9 12 15 `
- stop(frames=0)[source]#
Stops the board.
- Parameters:
frames (int, optional) – If
framesis set, board will be stopped in n frames. . Defaults to 0.
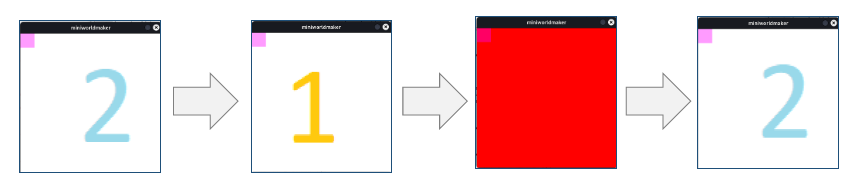
- switch_background(background)[source]#
Switches the background
- Return type:
- Parameters:
background – The index of the new background or an Appearance. If index = -1, the next background will be selected
Examples
Switch between different backgrounds:
from miniworldmaker import * board = Board() token = Token() board.add_background("images/1.png") board.add_background((255, 0, 0, 255)) board.add_background("images/2.png") @timer(frames = 40) def switch(): board.switch_background(0) @timer(frames = 80) def switch(): board.switch_background(1) @timer(frames = 160) def switch(): board.switch_background(2) board.run()
Output:
- Returns:
The new background
- switch_board(new_board)[source]#
Switches to another board
- Parameters:
new_board (Board) – _description_
- property tile_size: int#
Tile size of each tile, if board has tiles
- Returns:
The tile-size in pixels.
- property tokens: LayeredDirty#
A list of all tokens registered to the board.